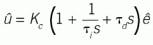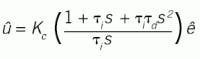Understand variations in the PID algorithm
When tuning a control loop or choosing an algorithm version that's consistent within your use context, it's important to understand the variations that exist in the proportional, integral, derivative (PID) algorithm. Unfortunately, there are many names for the several key versions of the algorithm, and names such as series or parallel are each applied to two distinctly different formulations. Accordingly, it's been best to identify the algorithm formulation by its calculus or Laplace representation, not the many names, to make clear distinctions.
To help unify the nomenclature, ISA Standards Committee 5.9 is suggesting uniform naming conventions for PID algorithms. This article is intended to update the reader on the committee’s current agenda, as well as reveal some of the commonly applied alternate names that you may be using.
The main three PID algorithms
Standard: a Laplace representation of the standard algorithm is:|This has been called parallel because the block diagram has the P, I and D operations in parallel. But it's also called series because in this mathematical form the controller gain multiplies each of the P, I, and D terms in series. It's called ideal because 1) it's the form that arises from controller synthesis and 2) it's the most convenient for mathematical analysis. It's been called the ISA standard, even though ISA hasn't declared any algorithm as such. It's also called non-interacting, or non-interactive, perhaps because it lacks that feature of the interacting controller. The ISA 5.9 committee is moving toward recommending this form be called “standard,” but not declaring this as the best or right way to formulate the P, I and D functions.
There are many versions of how this standard equation can be represented. If the terms inside the parentheses are combined, then it will appear as:About the Author
R. Russell Rhinehart
Control

Leaders relevant to this article: